About Gutenberg
WordPress community a long time ago has started a project called Gutenberg. The aim of this project is to enrich the user experience during the content editing process. Gutenberg WordPress editor is a page builder. WordPress gives you the option to install this feature in 4.9 version as a plugin. From version 5.0 and after Gutenberg will be embedded into the core of WordPress.
During all WordPress versions, the user was editing the content by using a simple editor. This editor was similar to Microsoft Word helping the user in this new content writing experience. Through this simple content editor, we could add text, images, links in order to enrich the page content and user experience. However, sometimes the user had to learn how to insert short pieces of code in order to add some extra functionality. Such an example is the embedded YouTube code which the user had to insert into the editor, some WordPress versions before. Additionally, the content structure was dependent on the theme structure so the content sometimes was not properly positioned.
Taking into consideration all these issues, the WordPress community has developed the Gutenberg editor. The goal of this change to provide users the ability to build content only by using visual components, without any restrictions.
What about WordPress 4.9.8 version
In version 4.9.8 WordPress offered an option to install the Gutenberg plugin in order to test it. This is the welcome Dashboard screen of the latest WordPress version, featuring the new content editor.

Though this page you can install the Gutenberg editor plugin, by clicking the Install Gutenberg button.
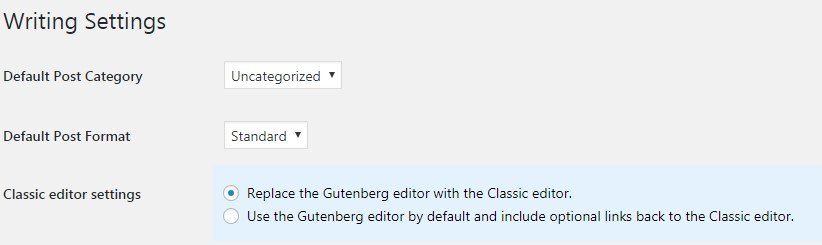
If you want to use the classic editor, then you can click the Install the Classic Editor button instead. In this case, you should access the Writing Settings and choose the “Replace…” option in order to let the classic editor replace Gutenberg which is the default one.
Gutenberg Editor’s blocks
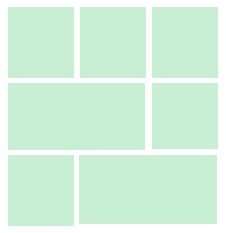
The basic component of the Gutenberg WordPress editor is called block(s). The user is able to insert and position an unlimited number of blocks in any order. Blocks are re-arranged by drag and drop. Every block has a specific functionality. For example, we can insert a text block and underneath of it, we can insert an image block.
Every block component has the following characteristics:
- Block manipulation options such as movement, delete or convert the specific block functionality to a similar one.
- Options to manipulate specific block functionality such as text options, image options, e.t.c.
The Gutenberg editor’s environment
When we create a new post/page we can see the following image.
The content editor environment consists of three basic parts:
- Editor bar. This is the top horizontal bar consists of document functionalities such as the publish option.
- Content area. This is the main editing area that occupies the maximum space of the document. In this area, you add your post/page content.
- Settings bar. This is the vertical bar on the right side of the Dashboard. In this bar, we can see options about the content block we selected to add/edit.
When we start a new document there is one block created by default. This is the block which we can use to insert the document’s title and edit the link of this.
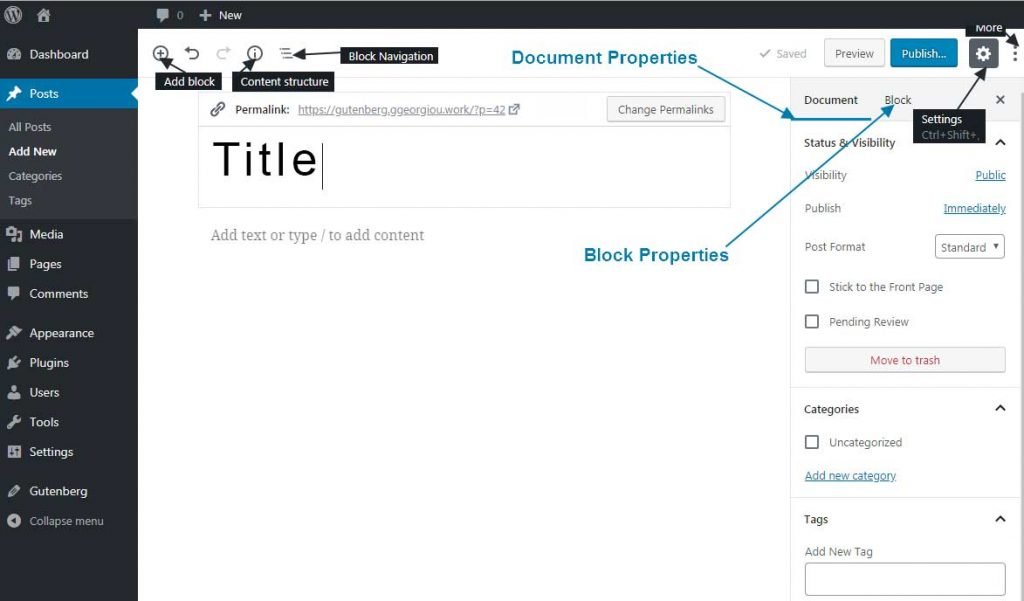
Editor Bar
Choosing the Add Block button (+ sign) we can see the following grouped block’s options.
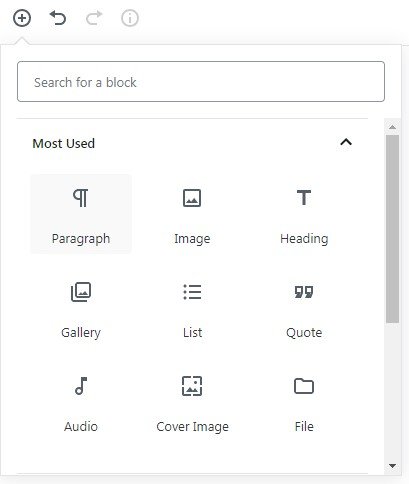
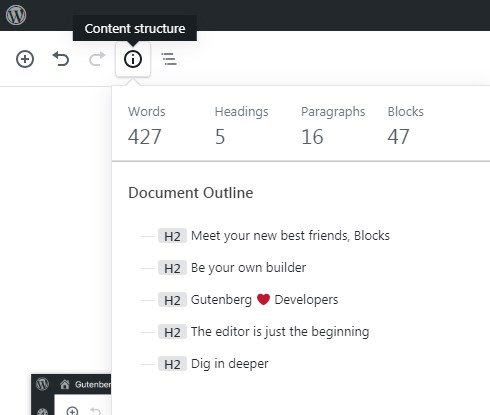
Content Structure option lets you take a look at the documents statistics like the headings number, the block’s number, e.t.c.
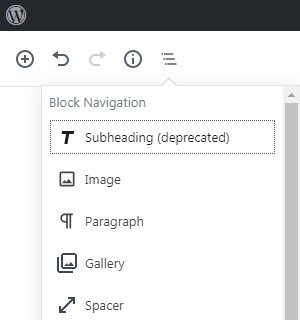
The Block Navigation option settings appear in a drop-down menu. Through this menu you can see existing blocks in the document in the order you have positioned them. By clicking on a block the screen scrolls until it finds the selected block on the document.
In far right part of the editor, you can find the Preview, Publish/Update page or post options. All of them operate the same way as in the classic WordPress editor. Same applies with the Settings option which lets you hide/show the properties bar on the right side of the page.
![]()
The last choice is called More and is presented with 3 vertical dots on the right side of the settings icon(gear).
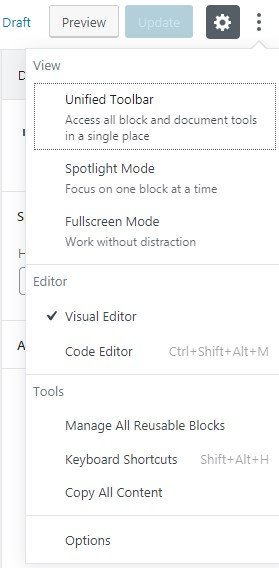
Some of the “More” options(view) are described below:
- Unified Toolbar: This option once selected it shows/hides a horizontal bar at the top of the editor. The bar consists of a few editing choices about the selected block.
- Spotlight Mode: This option is very helpful for long content editing since it highlights the editing block and pushes back the rest of the post/page content making it easier for an editor to work.
- Fullscreen mode: This option hides/shows the Dashboard bars(top and side).
Content Area
The content area is the main editing area of the Gutenberg WordPress editor. In this block, you can add your post/page content using a live editor which will simulate how your post/page will look like in the live site.
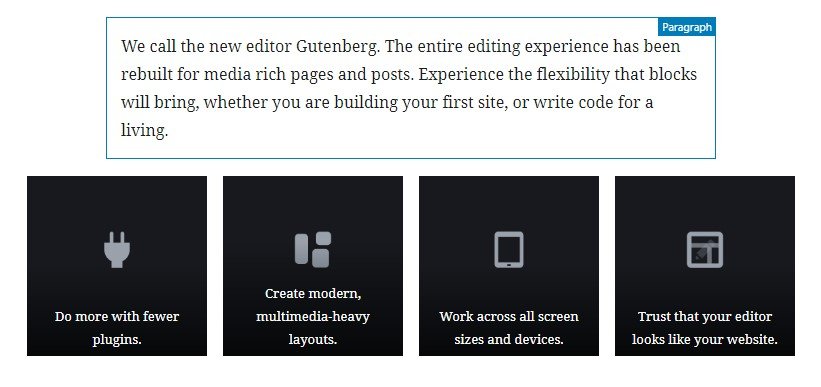
Moving the mouse pointer on the area of a block, you will notice see a thin border around it. You can also see the block’s type at the top-right corner of the block, i.e. paragraph.
If you activate the text block area a small formatting toolbar is enabled at the top of the widget, this is the quick toolbar. This toolbar holds a number of block operation options as well as content options.
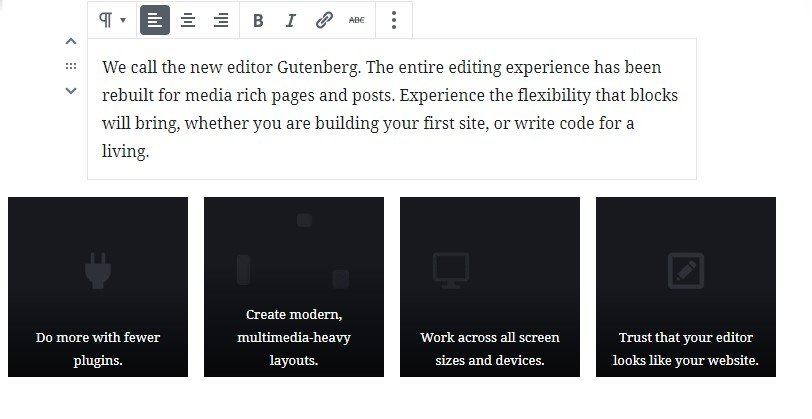
Block administration choices
The text block options can be revealed if you select the three vertical dots at the right end of the toolbar. When selected a new menu will drop down vertically with the text block options.
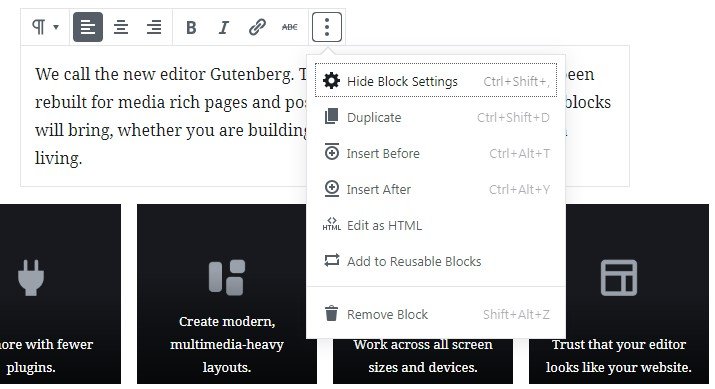
You can read more about these options below:
- Hide block settings: This option hides/shows the settings bar on the right side of the page.
- Duplicate: The duplicate option creates a copy of the selected block underneath.
- Insert Before: This option inserts a blank block before the selected one.
- Insert After: You can select this option if you want to insert a blank block after the selected one.
- Edit as HTML: This enables the HTML code editor for the selected text block.
- Add to reusable blocks: This option saves the current text block into an area called reusable blocks so that to reuse it again.
- Remove Block: Finally, this option removes the current text block completely.
On the left side of the quick bar there is an option which lets you transform the current block type to a different one:
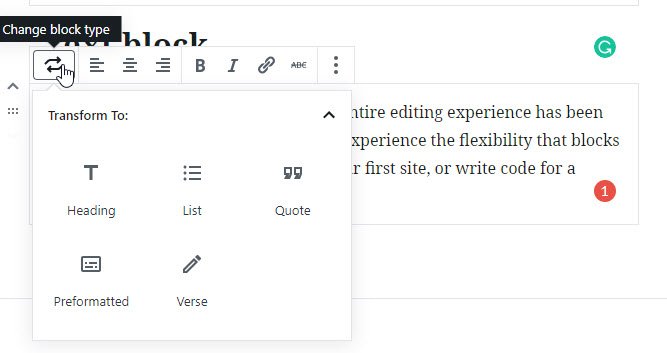
Using this option you can convert the type of the current block into something that uses a similar functionality.
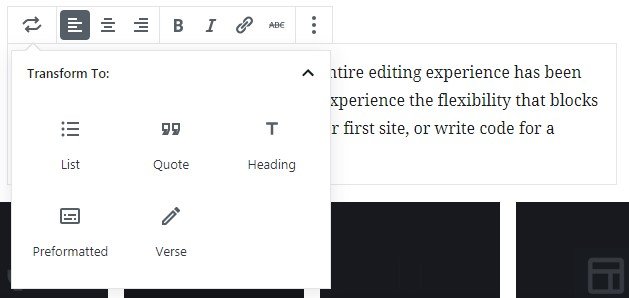
On the left side of the block, there are three buttons which can help us move the block vertically. These buttons appear also when hovering our mouse pointer on any other block except the one we’re currently active.
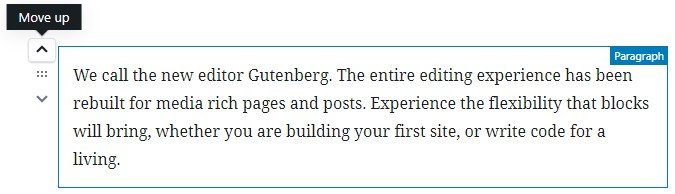
Block placement options are:
- Move Up: It moves the block one position up.
- Middle: This one lets you drag and drop the block in the desired position and order.
- Move Down: This option moves the block one position down.
Inserting a Gutenberg Block:
If you want to insert a Gutenberg block then you need to your mouse pointer on a block. Instantly you will notice a little cross (+) at the centre of the top border of the block. Select the Add Block icon and this way you’ll add a block at the selected position of your post/page.

In order to add a paragraph block select the plus sign icon at the top-right corner.
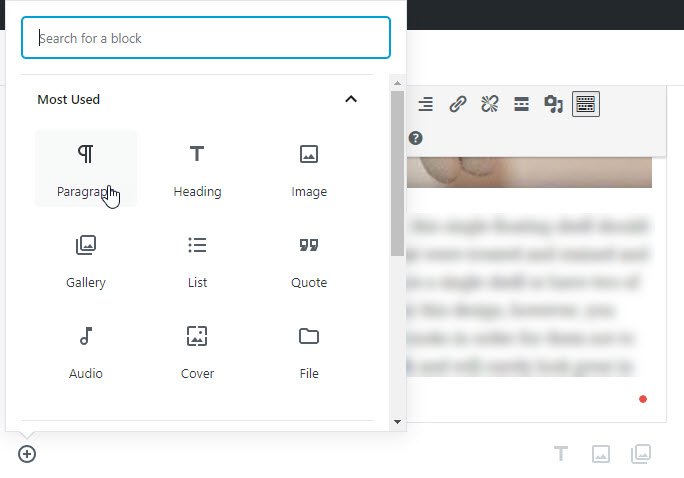
Then select the Paragraph option, just after you’ll see that the new paragraph block has been added. Next thing to do is to click on it and start writing your content.
Settings Bar
This bar is located on the top right side of the WordPress Gutenberg editor.
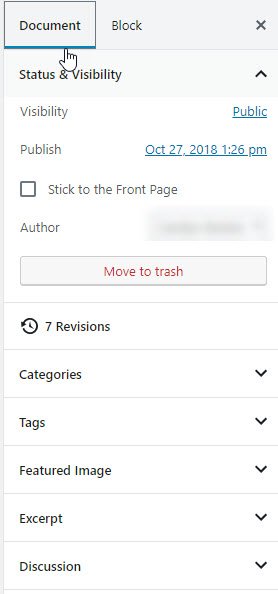
Once you select a block the Block Settings content, located next to the Document Settings tab, change accordingly. If we click outside a selected block, then on the settings bar we can see the document’s properties. These properties depend on the page post type that is post, page. For example:
Gutenberg WordPress Editor Useful Resources
You can try the new Gutenberg editing experience at the official site. Please visit also the following websites in order to learn more about Gutenberg:
- Official Gutenberg FAQ
- Gutenberg Handbook References
- Frontenberg, lets you test and try the Gutenberg editor as a guest.
- Resource website dedicated to Gutenberg WordPress Editor
Leave a Reply